While updating or downloading applications the download speed can sometimes be really bad. So it is important to select the nearest mirrors of ubuntu so you can enjoy the fastest download speeds. Also some cloud providers like Hetzner, Google Cloud add their own mirrors to the sources list and we face problems while installing many popular programs like docker, OpenJDK, etc.
There are times when we try to do sudo apt install docker.io or sudo apt install default-jre and we get the following error –
sudo apt install docker.io Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done E: Unable to locate package docker.io E: Couldn't find any package by glob 'docker.io' root@ubuntu-2gb-hel1-1:~# sudo apt install default-jre Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done E: Unable to locate package default-jre
This happens when the repository mirrors which are added in the server’s sources.list file does not contain these applications and can be fixed by simply changing to the appropriate sources.
Adding the official ubuntu mirrors to the sources.list file fixes this problem and we are able to install the programs.
How to select the fastest mirrors on Ubuntu?
There are three different ways you can use to find the fastest and nearest Ubuntu mirrors –
1. Use country code
If you are in the United States or Canada then you can just put ‘us ‘ or ‘ca’ in front of the URLs. In this way, you will connect to your country’s official Ubuntu repository mirror.
If you are in the United States just add us in front of all the URLs present in the sources.list file
deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted
Or if you are in Canada simply add ca in front of all the URLs
deb http://ca.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted
But this is always not the best solution because depending on your ISP, they might have different peering arrangements which can limit your download speeds.
2. Select mirrors manually
The next best solution is to manually find the best available mirrors and then add those to your sources file.
Type the following command on the command line –
$ wget -qO - mirrors.ubuntu.com/mirrors.txt
Then the nearest and fastest mirrors will be displayed. copy those and paste them in the sources file iin the correct format.
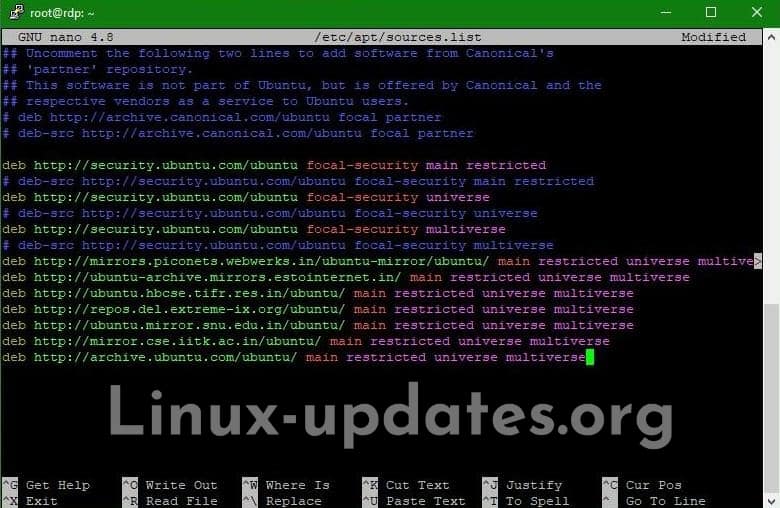
$ wget -qO - mirrors.ubuntu.com/mirrors.txt http://ubuntu.mirror.snu.edu.in/ubuntu/ http://ubuntu-archive.mirrors.estointernet.in/ http://mirror.cse.iitk.ac.in/ubuntu/ http://repos.del.extreme-ix.org/ubuntu/ http://mirrors.piconets.webwerks.in/ubuntu-mirror/ubuntu/ http://ubuntu.hbcse.tifr.res.in/ubuntu/ http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/
3. Use mirror protocol
Ubuntu supports are mirror protocol in the sources.list file which will automatically connect you to the nearest mirror. Replace the current source entry
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted
to
deb mirror://mirrors.ubuntu.com/mirrors.txt focal main restricted
Replace all the other entries in the file similarly in proper format as it was before.
How to update mirrors on the sources.txt file?
Follow these steps in order to update the sources.txt file –
- Log into your Linux VM as the root user.
- Open the sources.list file with nano.
- Now add or edit the sources in any way you want from the above three ways.
- Remember to add the sources in proper formats as it was already in the file. Also, remember to add the correct version name of Ubuntu which is currently installed. Here is a table with the names of the Ubuntu versions.
| Version | Name |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu 14.04 | Trusty Tahr |
| Ubuntu 16.04 | Xenial Xerus |
| Ubuntu 18.04 | Bionic Beaver |
| Ubuntu 20.04 | Focal Fossa |
| Ubuntu 20.10 | Groovy Gorilla |
| Ubuntu 21.04 | Hirsute Hippo |
- Save that file by pressing CTRL+X simultaneously and then ‘Y’.
- Now update
sudo apt update- You have now successfully updated the mirrors list.


